Dielectric Resonator
- Robert Fennis
- Jul 24, 2025
- 2 min read
Updated: Aug 18, 2025
In this blogpost, we will briefly look at the eigenmode solver in EMerge.
The simulation is based on the dielectric resonator design from the book "Microwave Filters for Communication Systems" by Richard J. Cameron et. al.
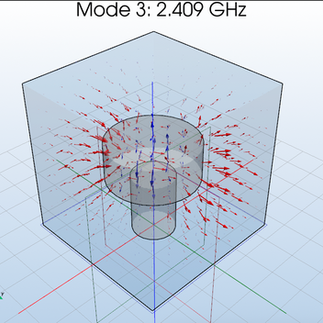
The design features a 2 by 2" box that is 2.03" tall. The support of the resonator has a 0.56" diameter and is 0.8" tall with an εᵣ = 10. The top resonator has a 1.176" diameter and a height of 0.481" with εᵣ = 34.
The diagrams in the book are copyrighted but the mode frequencies are:
Single Mode (TEH) = 1.931 GHz
Single Mode (TME) = 2.289 GHz
Dual Hybrid mode (HEH) = 2.414 GHz
And a dual hybrid mode (HEE) = 2.483 GHz
The simulation file is as following:
import emerge as em
mm = 0.001 # meter per millimeter
inch = 25.4 * mm # meter per inch
S = 2.03 * inch # enclosure height
W = 2.0 * inch # enclosure width/length (square base)
# Supporting block (substrate) dimensions
Dsup = 0.56 * inch # support cylinder diameter
Lsup = 0.8 * inch # support cylinder height
# Resonator cylinder dimensions
Dres = 1.176 * inch # resonator cylinder diameter
Lres = 0.481 * inch # resonator cylinder height
mat_support = em.lib.Material(er=10, color="#ffffff")
mat_resonator = em.lib.Material(er=34, color="#ededed")
Nmodes = 5
model = em.Simulation('DielectricResonatorFilter')
box = em.geo.Box(
W, W, S,
position=(-W/2, -W/2, 0)
)
support = em.geo.Cylinder(
radius=Dsup/2,
height=Lsup,
cs=em.GCS,
Nsections=20
).set_material(mat_support).prio_up()
resonator = em.geo.Cylinder(
radius=Dres/2,
height=Lres,
cs=em.GCS.displace(0, 0, Lsup),
Nsections=32
).set_material(mat_resonator).prio_up()
model.mw.set_frequency(3e9)
model.generate_mesh()
data = model.mw.eigenmode(
2e9,
nmodes=Nmodes
)
for mode_index in range(Nmodes):
# Extract field grid for this mode (sample spacing ~0.2 in)
field = data.field[mode_index].grid(0.2 * inch)
# Show enclosure, support, and resonator transparently
model.display.add_object(box, opacity=0.1)
model.display.add_object(support, opacity=0.3)
model.display.add_object(resonator, opacity=0.3)
# Plot E-field vectors in red and H-field vectors in blue
Evec = field.vector('E', 'real')
Hvec = field.vector('H', 'real')
model.display.add_quiver(*Evec, color='red')
model.display.add_quiver(*Hvec, color='blue')
# Annotate resonant frequency and field labels
freq_ghz = data.field[mode_index].freq.real / 1e9
model.display.add_title(f'Mode {mode_index+1}: {freq_ghz:.3f} GHz')
model.display.add_text('E-field', color='red', abs_position=(0, 0.95))
model.display.add_text('H-field', color='blue', abs_position=(0, 0.9))
# Render each mode one at a time
model.display.show()
The results are as following: